The most secure monetary network in the world
News!
Chainalysis refutes Binance’s illicit volume report due to omitted data
The post Chainalysis refutes Binance’s illicit volume report due to omitted data appeared on…
What Is KYC in Crypto? (Meaning & Guide In 2025) – CryptoNinjas
The post What Is KYC in Crypto? (Meaning & Guide In 2025) – CryptoNinjas…
South African Reserve Bank Eyes Wholesale CBDC Over Retail, Flags Crypto Risks
The post South African Reserve Bank Eyes Wholesale CBDC Over Retail, Flags Crypto Risks…
6.3 Million Viewers Tune In For 30th Anniversary Reunion
The post 6.3 Million Viewers Tune In For 30th Anniversary Reunion appeared on BitcoinEthereumNews.com….
USD/JPY slips as Yen gains on intervention talk, US data disappoints
The post USD/JPY slips as Yen gains on intervention talk, US data disappoints appeared…
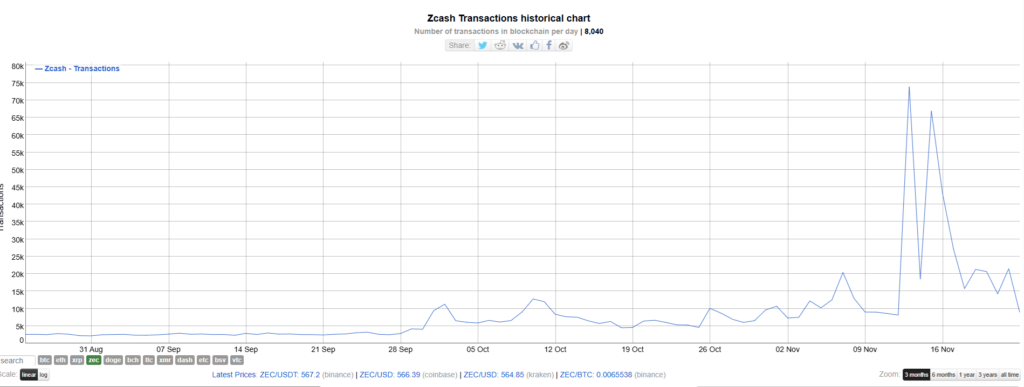
ZCash chain posts peak mining, transaction activity in November, beats Ethereum and Solana
The post ZCash chain posts peak mining, transaction activity in November, beats Ethereum and…
Introduction to Bitcoin: Discover the transformative power of Bitcoin (BTC), the pioneering cryptocurrency revolutionizing traditional financial systems. Launched in 2009 by the enigmatic Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin offers a decentralized alternative to conventional currency, enabling seamless peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. Explore the core principles of Bitcoin, its underlying blockchain technology, and the lucrative opportunities it presents.
Understanding Bitcoin’s Origins: Delve into the origins of Bitcoin, tracing back to the registration of Bitcoin.org in August 2008. Learn about the visionary white paper published by Nakamoto in October 2008, laying the groundwork for Bitcoin’s groundbreaking peer-to-peer electronic cash system. Explore the significance of the first mined block on January 3, 2009, and the subsequent halving events shaping Bitcoin’s reward structure.
Unveiling Bitcoin’s Blockchain Technology: Unlock the secrets of Bitcoin’s blockchain, a distributed ledger system powered by cryptographic techniques. Discover how each block in the blockchain stores transaction data, linked together to form an immutable chain. Gain insights into the SHA-256 hashing algorithm, ensuring the integrity and security of Bitcoin transactions.
Navigating Bitcoin Mining: Embark on a journey through Bitcoin mining, the process of validating transactions and securing the network. Explore the evolution of mining hardware, from personal computers to specialized Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs). Learn about the benefits of joining mining pools and the potential returns from participating in Bitcoin mining activities.
Why Bitcoin?
In a world where traditional money like the dollar, the euro, the yen, and most fiat currencies constantly lose value due to their infinite printing and the growing debt of states, Bitcoin emerges as a solution. Unlike conventional currencies, Bitcoin does not depend on governments or central banks. Its supply is limited by an immutable code, ensuring that no more can be created, and thus it retains its value over time. While fiat money loses purchasing power due to its nature and the decisions of governments, Bitcoin follows clear mathematical rules that are open to everyone. In this way, it offers a stable alternative to protect wealth.
Key Points that Benefit Bitcoin:
- Limited Supply: Bitcoin has a fixed supply of 21 million coins, making it immune to inflation and excessive money printing like the USD.
- Accessibility: Bitcoin can be accessed and transferred globally without intermediaries, making it easy to use worldwide.
- Transaction Speed: Unlike USD and gold, Bitcoin allows for fast and cheap global transactions.
- Transparency: Bitcoin’s code is fully open and accessible, allowing anyone to verify the system and transactions.
- Risk of Confiscation: While USD and gold can be seized by governments or require secure storage, Bitcoin provides full control over your funds if private keys are managed properly.
These features make Bitcoin a unique alternative to traditional assets in an increasingly digital and decentralized world.
Asset comparison against Bitcoin
The “Asset Class Total Returns Since 2011” table shows that Bitcoin (BTC) has been the top-performing asset in recent years. Despite its high volatility, with significant declines in certain periods (-58% in 2014 and -73% in 2018), Bitcoin has achieved a cumulative return of 1,888,169% and an annualized return of 145.9%.
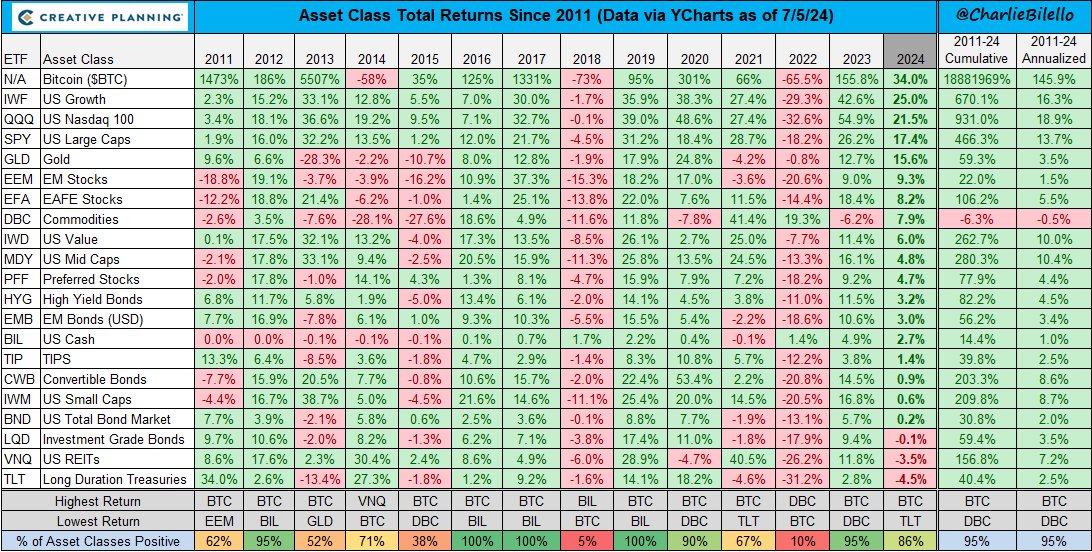
In comparison, other assets like the Nasdaq 100 (QQQ) and US Growth (IWF) have also delivered solid performance, with annualized returns of 18.9% and 16.3%, respectively. However, these figures are far from the results achieved by Bitcoin.
In summary:
- Bitcoin has delivered the highest returns, though with significant volatility.
- Other assets, such as bonds and traditional equities, have provided greater stability but lower returns.
The table highlights a clear reality: in terms of returns since 2011, Bitcoin has outperformed all other asset classes.
Bitcoin as an Investment: Solving Inflation and Demonetizing Real Estate, Gold, and Commodities
1. The Problem of Inflation
Understanding Inflation
Inflation occurs when there is an expansion of the money supply without a proportional increase in goods and services production. This erodes the purchasing power of money over time. Fiat currencies (such as the dollar, euro, etc.) depend on centralized monetary policies, which can lead to:
- Uncontrolled issuance of money by central banks.
- Constant reduction in the value of money over time (structural inflation).
- Loss of trust in the currency (extreme cases like hyperinflation).
How Does Bitcoin Solve This Problem?
- Limited and Programmed Supply: Bitcoin has a finite supply of 21 million units, making it a deflationary asset. Unlike fiat currencies, it cannot be issued arbitrarily.
- Halving Mechanism: Bitcoin issuance decreases by half approximately every 4 years, further restricting supply growth.
- Preserving Purchasing Power: Bitcoin’s digital scarcity allows it to serve as a long-term store of value, similar to gold but with superior characteristics (portability, divisibility, and resistance to confiscation).
2. Demonetizing Gold
The Traditional Role of Gold as a Store of Value
Historically, gold has been used as protection against inflation and as a safe haven in times of uncertainty. However, gold has significant drawbacks:
- Difficult to Transport: Physical gold is heavy, bulky, and hard to move.
- Storage and Security Costs: Storing gold involves significant expenses for custody.
- Limited Divisibility: Gold is impractical for small transactions.
- Risk of Counterfeits and Centralization: There is a risk of counterfeit gold or centralization in government reserves.
Bitcoin as an Alternative to Gold
- Digital and Portable: Bitcoin can be transferred anywhere in the world instantly, regardless of amount.
- Low Storage Costs: It only requires cryptographic keys and a digital wallet.
- Censorship Resistant: Governments cannot easily confiscate Bitcoin due to its decentralized nature.
- Highly Divisible: Bitcoin can be divided into 100 million units (satoshis), enabling transactions of any size.
- Transparent and Auditable: Bitcoin’s network allows public and decentralized verification of all transactions.
This makes Bitcoin a more efficient and attractive “digital gold” for the modern economy.
3. Demonetizing Real Estate
Problems with Real Estate as a Monetary Investment
In inflationary economies, people often turn to real estate as:
- A long-term store of value.
- Protection against currency devaluation.
However, investing in real estate has notable challenges:
- High Entry Barriers: Significant capital is required to purchase properties.
- Low Liquidity: Selling a property can take weeks or months.
- Maintenance and Regulation Costs: Taxes, repairs, and regulations impact profitability.
- Centralization and Confiscation Risk: Governments can impose restrictions or expropriate real estate.
Bitcoin as an Alternative to Real Estate
- Accessible to All: Bitcoin does not require large amounts of capital; it can be bought in fractions.
- Highly Liquid: Bitcoin can be bought and sold 24/7 in global markets.
- Portable and Secure: Bitcoins can be moved anywhere without physical or regulatory restrictions.
- No Maintenance Costs: There are no repair, annual tax, or management expenses.
- Protection Against Confiscation: Bitcoin is a digital asset that cannot easily be seized by governments.
This enables Bitcoin to “demonetize” real estate by offering a more liquid, efficient, and accessible store of value.
4. Demonetizing Commodities
Commodities as a Store of Value
Assets like oil, industrial metals, or food have also been used as hedges against inflation. However:
- Volatility: Commodity prices fluctuate dramatically due to external factors (demand, geopolitics, weather, etc.).
- Storage and Transport Costs: Physically maintaining commodities is costly and inefficient.
- Complex Investment: Commodities are not easily accessible to the average investor due to logistical and technical barriers.
Bitcoin as an Alternative to Commodities
- Immutable and Uncorruptible: Bitcoin does not depend on external factors like production, demand, or physical storage.
- Highly Liquid and Globally Accessible: Anyone with internet access can invest in Bitcoin.
- Greater Predictability: Bitcoin’s limited and programmed supply eliminates uncertainties about its future availability.
- Resilient to External Volatility: While Bitcoin can be volatile, it is not subject to risks like wars, climate, or natural disasters.
5. Bitcoin as a Systemic Solution
Bitcoin not only addresses problems of inflation and demonetizes traditional assets; it also tackles structural flaws in the financial system:
- Decentralized System: It removes dependence on financial institutions and governments.
- Global Peer-to-Peer Transactions: It facilitates fast and low-cost payments between individuals worldwide.
- Financial Inclusion: Bitcoin allows unbanked individuals to access a store of value and medium of exchange.
General Conclusion
Bitcoin represents a disruptive solution to the problems of fiat money and inflation. By demonetizing traditional assets like gold, real estate, and commodities, Bitcoin offers unique characteristics:
- Programmed Scarcity
- Global Portability
- High Liquidity and Divisibility
- Censorship and Confiscation Resistance
As a result, Bitcoin has the potential to become the “ultimate store of value” in the digital era, transforming the global economy into a more efficient, fair, and accessible system for all.
Current Ways to Buy or Gain Exposure to Bitcoin
Today, there are several ways to purchase or gain exposure to Bitcoin, each with varying levels of complexity, risks, and benefits. Below, we break them down, starting with the simplest options and progressing to the more advanced ones:
1. Bitcoin ETFs
How It Works:
A Bitcoin ETF (Exchange-Traded Fund) allows investors to gain indirect exposure to Bitcoin without owning or managing it directly. These funds track Bitcoin’s price and are traded on regulated markets, just like stocks. Examples include:
- ProShares Bitcoin Strategy ETF (BITO)
- Valkyrie Bitcoin ETF (BTF)
- Futures-based ETFs regulated by CME Group.
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Ideal for traditional investors who don’t want to deal with private keys or custody.
- Regulation: ETFs offer a trusted structure under market supervision.
- Accessibility: Can be purchased through any traditional brokerage.
Risks:
- No Real Ownership: You don’t own Bitcoin directly; you only hold its representation in the ETF.
- Tracking Error: Futures-based ETFs may not perfectly replicate Bitcoin’s price.
- Fees: ETFs often charge annual management fees.
- Counterparty Risk: You rely on the fund manager and the stability of the market.
2. MicroStrategy (MSTR) Stock
How It Works:
MicroStrategy (MSTR), led by Michael Saylor, operates as a leveraged Bitcoin holding company. The firm uses its balance sheet to acquire massive amounts of Bitcoin and finances this strategy with debt. Buying MSTR shares gives investors exposure to Bitcoin with a leveraged effect.
Advantages:
- Leverage to Bitcoin: Due to its debt-financed strategy, MSTR shares amplify Bitcoin’s price movements.
- Easy Access: MSTR is traded on regulated stock exchanges (NASDAQ) and accessible through brokers.
- Liquidity: Shares can be easily bought and sold on the market.
Risks:
- Extreme Volatility: Leverage magnifies both gains and losses.
- Business Risk: While Bitcoin dominates MicroStrategy’s strategy, it remains a stock subject to operational and debt risks.
- Dependency on Bitcoin: If Bitcoin’s price drops, MSTR stock will be significantly impacted.
- Share Dilution: The company may issue new shares to finance further Bitcoin acquisitions.
3. Direct Bitcoin Purchase on Exchanges
How It Works:
Centralized exchanges like Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, or Bitstamp allow you to purchase Bitcoin directly with fiat currencies (USD, EUR, etc.). Once purchased, you can keep Bitcoin on the exchange or transfer it to a private wallet.
Advantages:
- Real Ownership: You buy and own the asset directly.
- Liquidity: Exchanges offer high liquidity for transactions of any size.
- User-Friendly Platforms: Exchanges provide intuitive interfaces and global access.
Risks:
- Centralized Custody: Keeping Bitcoin on exchanges exposes it to hacks or fraud (e.g., FTX, Mt. Gox).
- Regulatory Restrictions: Governments may restrict or block access to centralized exchanges.
- Privacy Concerns: Exchanges require KYC verification, compromising privacy.
- Potential Confiscation: Authorities can freeze exchange accounts.
4. Bitcoin Purchase on Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Platforms
How It Works:
Peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms allow individuals to buy Bitcoin directly from each other without intermediaries. Examples include Paxful, LocalBitcoins, or Binance P2P.
Advantages:
- Increased Privacy: Some platforms don’t enforce strict KYC processes.
- Payment Flexibility: Transactions can be completed using cash, bank transfers, PayPal, etc.
- Access in Restricted Regions: Ideal for countries with exchange restrictions.
Risks:
- Fraud and Scams: There’s a risk the other party won’t fulfill their end of the transaction.
- Low Liquidity: Large Bitcoin purchases may be challenging on P2P platforms.
- Lack of Escrow: Without escrow protection, funds could be lost.
- Regulatory Issues: Some jurisdictions may prohibit or restrict P2P transactions.
5. Self-Custody of Bitcoin in Private Wallets
How It Works:
After purchasing Bitcoin on an exchange or through P2P platforms, you can transfer it to a private wallet where you control the private keys. Wallet options include:
- Hardware wallets: Physical devices like Ledger or Trezor.
- Software wallets: Applications like Electrum or Exodus.
- Paper wallets: Printed copies of your private keys.
Advantages:
- Full Control: You have complete ownership of your Bitcoin.
- Security: Reduces risks of exchange hacks or theft.
- Confiscation Resistance: No one can access your Bitcoin without your private keys.
Risks:
- Loss of Private Keys: Losing your keys means losing your Bitcoin permanently.
- Human Error: Sending Bitcoin to the wrong address is irreversible.
- Physical Theft: Hardware or paper wallets can be stolen.
- Neglected Backups: Failure to create secure backups can lead to loss.
6. Bitcoin Derivatives: Futures and Options
How It Works:
Derivatives such as futures and options provide exposure to Bitcoin’s price movements through platforms like CME Group, Binance Futures, or Deribit. Traders can use leverage to amplify their positions.
Advantages:
- Leverage Opportunities: Allows traders to achieve large returns with minimal capital.
- Risk Management: Derivatives can hedge existing Bitcoin investments.
- Liquidity: Derivatives markets have high trading volumes.
Risks:
- High Volatility and Liquidation: Leverage amplifies losses and can force position liquidations.
- Complexity: Derivatives require advanced trading knowledge and risk management.
- Counterparty Risk: Exposure to platform solvency issues.
- Potential for Significant Losses: Market movements against your position can lead to total losses.
Conclusion
There are multiple ways to gain exposure to Bitcoin, each with varying levels of risk, complexity, and control:
- Bitcoin ETFs (simplest and regulated).
- MicroStrategy Stock (MSTR) (leveraged exposure).
- Direct Purchase on Centralized Exchanges (real ownership).
- Peer-to-Peer Platforms (greater privacy).
- Self-Custody in Private Wallets (maximum sovereignty and security).
- Bitcoin Derivatives (high risk, high reward, and complexity).
The best method depends on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and knowledge level. Always prioritize security and choose a strategy that aligns with your financial profile.
Comparison Between Bitcoin Auditing and Gold Auditing
Auditing is a key aspect of ensuring transparency and trust in financial assets. In this analysis, we compare Bitcoin auditing with gold auditing, highlighting challenges, differences, and cases of controversy.
1. Bitcoin Auditing
Transparency and Verifiability
- Bitcoin operates on a public blockchain, where all transactions are visible and verifiable in real-time by anyone.
- The total supply of Bitcoin is fixed at 21 million units, making its supply known and auditable at all times.
- Blockchain explorers like Blockchain.com or mempool.space allow users to verify transactions and address balances.
Auditing Methods
- Any user can audit the system by running a full Bitcoin node, validating every block since the genesis block.
- Independent audits can be conducted through proof-of-reserves, where exchanges and custodians demonstrate possession of their BTC.
- Bitcoin auditing does not rely on third parties; it is a decentralized and self-sufficient verification system.
Controversial Cases
- Cases like Mt. Gox in 2014 and FTX in 2022 highlighted the importance of proof-of-reserves to prevent fraud and mismanagement.
- Scalability solutions like the Lightning Network present traceability and auditing challenges compared to Bitcoin’s base layer.
- Despite being a transparent network, authorities have successfully traced fraudulent transactions. For instance, the 2016 Bitfinex hack saw the FBI track and recover part of the stolen funds in 2022.
- In 2021, Colonial Pipeline paid a Bitcoin ransom following a ransomware attack, but the FBI tracked the involved addresses and recovered part of the amount.
2. Gold Auditing
Transparency and Verifiability
- Gold auditing is a centralized process, dependent on central banks, national reserves, and private entities.
- There is no global public record of every gram of gold, making full verification of its supply difficult.
- Cases of counterfeit or impure gold (such as tungsten-filled bars) have been reported.
Auditing Methods
- Periodic audits of gold reserves in central banks and storage vaults, conducted by governmental or private entities.
- Purity tests, weighing, and serial number verification of gold bars.
- Some gold-backed ETFs allow periodic audits, but these remain closed processes to the public.
Costs and Transfer Issues with Gold
- Gold is expensive to transport due to its weight and the need for extreme security.
- International shipments require certifications, high logistical costs, and specialized insurance.
- Many investors prefer to leave their gold in vaults rather than take physical possession due to these inconveniences.
- Regulatory barriers in some countries complicate gold import/export.
Controversial Cases and Historical Frauds
- The Fort Knox Mystery: The last public audit of the U.S. gold reserves at Fort Knox was in 1953. Since then, theories have emerged about the possible depletion or disappearance of part of the stored gold.
- Rehypothecated Gold Scandal: Some gold reserves have been used as collateral in multiple financial contracts, raising concerns about their actual availability.
- Counterfeit Gold: In 2020, fake gold bars were discovered in China and in vaults of prestigious financial institutions.
- Bre-X Mining Fraud: In the 1990s, Canadian mining company Bre-X claimed to have discovered one of the largest gold deposits in the world in Indonesia, only for it to be revealed later that the samples had been tampered with.
- Gold ETF Fraud Concerns: Doubts have arisen about whether certain ETFs actually possess all the gold they claim to back, as auditing is not always transparent.
3. Comparison and Summary Table
| Feature | Bitcoin | Gold |
|---|---|---|
| Public Auditing | Yes, real-time via blockchain | No, depends on private/governmental entities |
| Historical Record | Complete and accessible | Incomplete, fragmented |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized | Centralized in banks and reserves |
| Verifiable Supply | Yes, 21 million BTC | No, subject to opacity and possible manipulation |
| Fraud Cases | Exchange collapses, lost keys, fraud tracing | Rehypothecated gold, counterfeit bars, mining scams |
| Verification Method | Blockchain explorers, full nodes | Physical and chemical audits |
| Last Major Audit | Ongoing, real-time | Fort Knox: 1953 |
| Storage Costs | Low, digital storage | High, requires security and transportation |
| Transfer Issues | Fast, seamless globally | Expensive and complex, with legal restrictions |
Conclusion
Bitcoin significantly outperforms gold in terms of transparency, verifiability, and decentralized auditing. While anyone can audit Bitcoin’s supply and transaction history at any time, gold auditing remains an opaque, centralized process with multiple controversies.
However, gold remains a tangible asset with thousands of years of history as a store of value, giving it an edge in historical trust. The lack of a clear global audit for gold strengthens Bitcoin’s case as an auditable and reliable alternative in the 21st century. At the same time, Bitcoin is not without issues, particularly regarding security on centralized platforms and fraud cases, although blockchain traceability has enabled the recovery of stolen funds in multiple instances.
-Michael Saylor-